After fishing of specimens onto slides, excess water must be drained out before placing on the hotplate for 3 minutes to melt off the wax. Then, it can be loaded into a rack for staining.
H&E staining
Principle: The purpose is to demonstrate the tissue constituents in contrasting colours. Hamatoxylin gis oxidised to haematein in the presence of an oxidising agent. Haematein is taken up by nucleic acids present in the nuclues in the presence of a mordant which are usually metallic salts that is able to chelate the haematein dye to the tissue component. Eosin stains the cytoplasm and connective tissue pink.
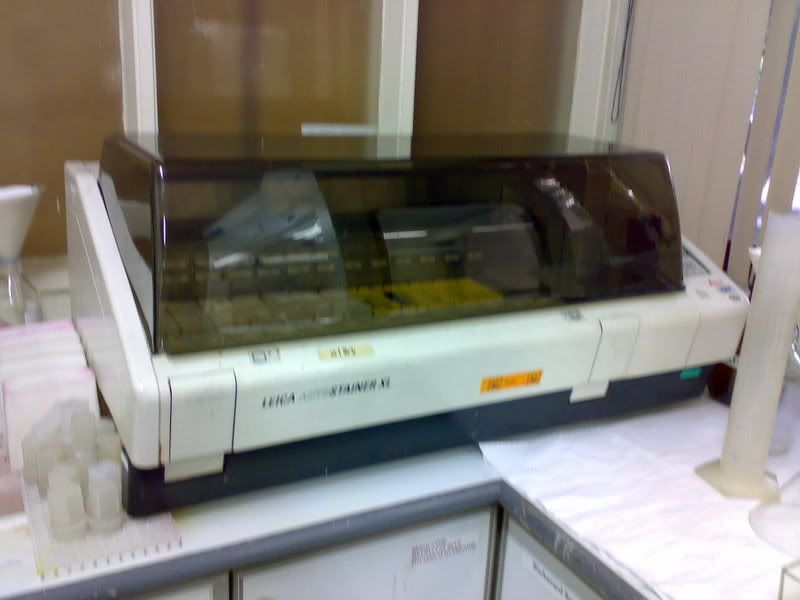
For routine H&E staining, the process is fully automated with the help of this machine (Leica Autostainer XL):
 Extracted from:http://www.spencerscicorp.com/html/slidestain.html
Extracted from:http://www.spencerscicorp.com/html/slidestain.html
This is how it works: After loading the rack into the machine, press LOAD and check that the machine is programmed to routine H&E staining. After that, the whole staining process will be carry out by the machine in this format:
1) Xylene--> 2 minutes
2) Xylene--> 2 minutes
* Steps 1 & 2- remove wax that has not melt off as wax are not water soluble.
3) Abs alcohol--> 1 minute
4) 95% alcohol--> 1 minute
5) 70% alcohol--> 1 minute
*Steps 3-5- remove xylene and rehydrate the specimens
6) Water--> 1 minute
*As haematoxylin (Hx) is aqueous based, must wash with water first
7) Hx--> 4 minutes
8) Hx--> 3 minutes
* Steps 7 & 8- stain the whole specimen 9)
9) Water--> 1/2 minute
10) 0.5% acid alcohol--> 2 dips
* Differentiation- remove excess Hx
11) Water--> 1 minute
12) Lithium carbonate--> 2 minutes
* An alkali which blue the specimen when place in water
13) Water--> 2 miuntes
* Blue in water
14) Water--> 3 minutes
15) Eosin--> 1/2 minutes
* Stains cytoplasm
16) 70% alcohol--> 1 minute
17) 95% alcohol--> 1 minute
18) 4 rounds of abs alcohol--> each for 1 minute
* Steps 16-18- dehydration as water cannot mix with xylene)
19) 3 rounds of xylene--> each for 1 minute
* Remove alcohol as depex used for mounting is xylene-based and also to raise refractive index of tissue
Results:
- Nucleur component- blue
- Cytoplasmic component- red
After the above process, the specimens will be send for mounting which is also automated.
Special staining
Principle: Some cases need special stains for diagnosis. H&E is not able to demonstrate the desired components.
Types of special stains:
- Periodic Acid Schiff
- GMS Fungus
- Reticullum ll
- Alcian Blue
- Iron
- Giemsa
- Congo Red
- Gram
1) Print barcode label(s) (according to biopsy number assgined to the specimen)
2) Paste lable(s) on the frosted end of the slide
3) Dewax and hydrate slide
4) Load the slide covered with special wash solution to prevent the specimen from drying up into the instument
5) Load appropriate stain kit into the reagent carousel (depending on the type of stains)
6) Select Run
* Pre-checklist will appear. Ensure all slides and reagent kit are in place. Cap of reagent kit must be open.
7) Enter number of slides and hit the Run button
The machine will now initiate the staining by reading the slide and reagent barcode labels. After the barcodes are read, information for the staining will be 'downloaded' from the NexES computer to the staining module and the run will resume. When the run has completed, click 'SIGN OFF' and remove the slides from the instument. Drain slides then load into rack and place in 95% alcohol to remove residual liquid before dehydration, clearing and mounting.
Manual Staining
Principle: The Ventana NexES machine are not able to carry out some special stains. An example is the Ziehl Neelsen staining. (I only perform this manual staining so far)
Tuberculosis Test/ Ziehl Neelsen:
Principle:To demomonstrate acid fast bacteria belonging to the genus mycobacterium responsible for causing tuberculosis. (diagnosis test for tuberculosis)
Control: Any tissue containing acid fast organism.
Reagents required:
- Commercial TB colour carbo reagent--> stains tubercle bacilli red
- Loeffler's Methylene Blue--> background staining
- 1% potassium hydroxide
- 1% acid alcohol
Procedures:
1) Dewax and bring sections to water
2) Stain with commercial TB colour carbo reagent for 5 minutes
3) Wash in running water
4) Differentiate with 2 rounds of 1% acid alcohol until colourless (patient is negative), light pink (patient is positive)
5) Wash in water
6) Counterstain with 1% Loeffler's methylene blue for 10-15 seconds
7) Wash in water and go to 95% alcohol to control intensity of the blue colour
*if very blue, go to 70% alcohol (the more diluted the alcohol, the greater the differentiation)
8) Check under microscope, if too much blue has gone off due to differentiation, repeat steps 6&7
9) Dehydrate in absolute alcohol, clear in 3 rounds of xylene and mount
Results: - Positve- red tubercle bacilli on blue background
- Negative- sky blue
Finally, its the end of my long posting. LOL. Feel free to ask me any easy questions. Hope you guys continue to learn more from SIP! Take care.=)
June Tham
TG02
0505073G